Quantitative Flow Ratio (QFR) is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that uses advanced computational algorithms to assess blood flow in the coronary arteries. QFR provides a functional assessment of the coronary arteries, allowing doctors to accurately identify significant narrowing or blockages in the arteries.
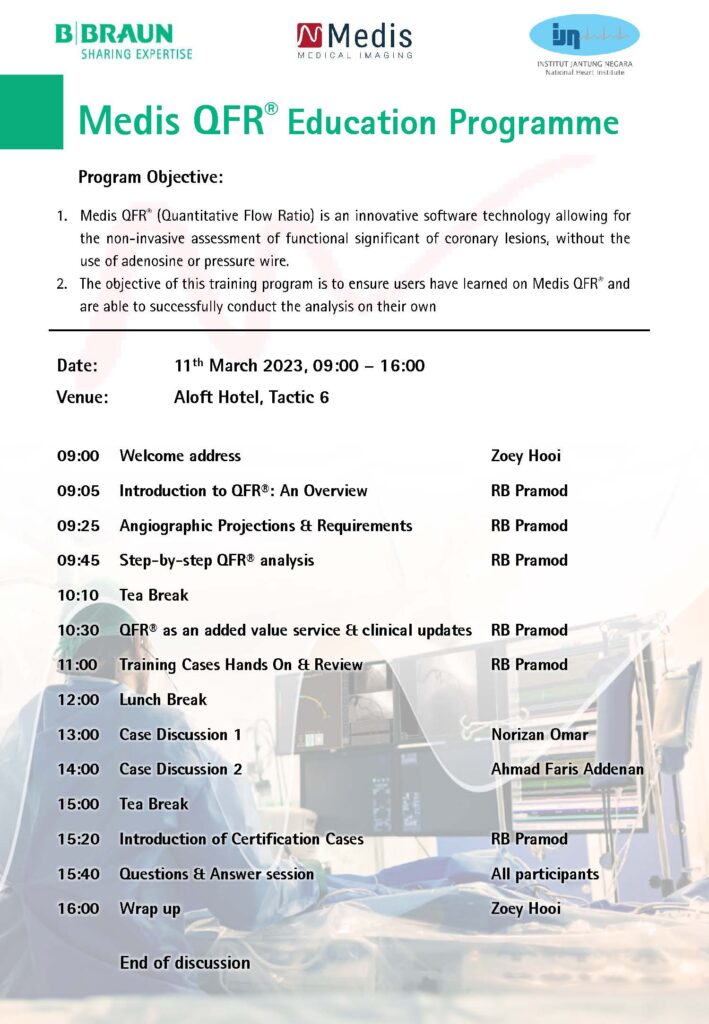
Traditional diagnostic methods for coronary artery disease, such as angiography, are invasive and require the use of contrast dye. QFR, on the other hand, uses only a routine angiogram to create a 3D model of the coronary arteries. The model is then analyzed using specialized software to determine the blood flow in each segment of the artery.
QFR works by simulating blood flow in the coronary arteries under various physiological conditions. By analyzing the flow parameters, the software can identify areas of the artery that may be significantly narrowed or blocked. This information can help doctors determine the best course of treatment for patients with coronary artery disease.
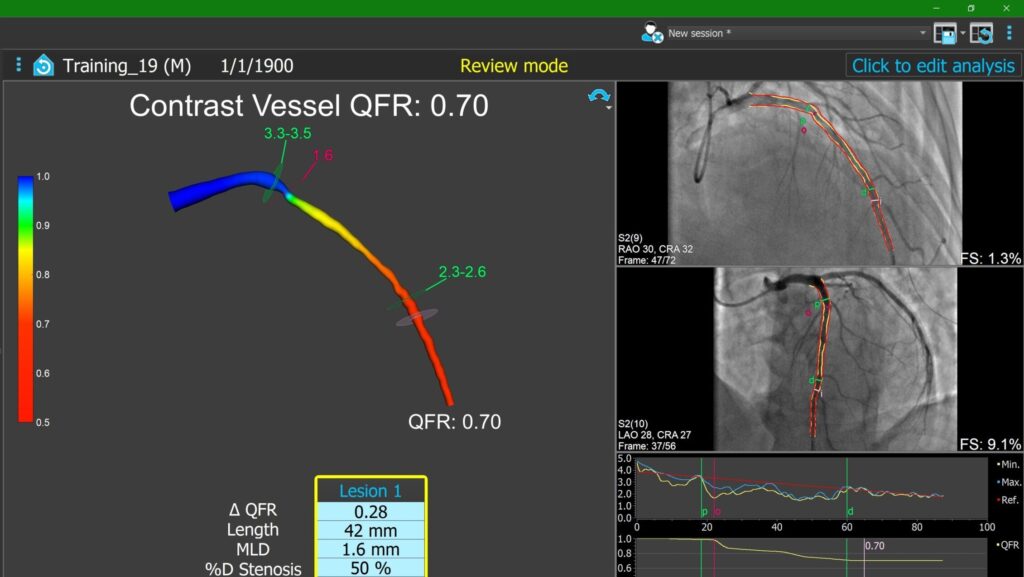
One of the benefits of QFR is that it provides accurate and reliable results with a high level of precision. Studies have shown that QFR is as effective as invasive methods such as fractional flow reserve (FFR) in assessing coronary artery disease.
Another advantage of QFR is that it is a non-invasive procedure, which means that it does not require the use of contrast dye or any other invasive techniques. This makes QFR a safer and more convenient option for patients, as there is no risk of complications or side effects associated with invasive procedures.
Overall, QFR is a promising diagnostic tool that can help doctors accurately assess blood flow in the coronary arteries and identify significant narrowing or blockages. With its high level of precision and non-invasive nature, QFR is becoming an increasingly popular option for patients with suspected coronary artery disease.
